Content
- 1 What is glucose and what is it for
- 2 The benefits of glucose for the body
- 3 What foods contain glucose
- 4 Daily intake
- 5 Normal blood glucose
- 6 Symptoms of a lack of glucose in the body
- 7 Why high blood glucose is dangerous
- 8 Nutrition for hyperglycemia
- 9 Instructions for the use of glucose tablets
- 10 Side effects
- 11 Contraindications to the use of glucose
- 12 Conclusion
A person replenishes energy due to the intake of useful microelements, macronutrients, vitamins, as well as fats, carbohydrates and proteins along with food. It is known that carbohydrates are one of the main energy components. The benefits and harms of glucose contained in carbohydrates are due to its properties.

What is glucose and what is it for
Glucose is the simplest monosaccharide among carbohydrates, which has 1 sugar molecule. Other monosaccharides include:
- ribose;
- galactose;
- fructose.
Glucose literally translated from Greek means "sweet". In another way, it is also called dextrose or grape sugar. In nature, glucose is found in the juice of fruits and berries. The benefit of the substance lies in the fact that glucose is also considered the main product of photosynthesis.
The molecule that makes up dextrose is part of the so-called complex sugars:
- polysaccharides (cellulose, glycogen, starch);
- disaccharides (lactose, maltose, sucrose).
Glucose is the end product of the breakdown (hydrolysis) of basic complex sugars. In particular, disaccharides that enter the stomach break down into fructose and glucose.

The following properties are distinguished:
- crystal-like substance;
- lack of pronounced color and smell;
- the presence of a sweet taste;
- solubility in water.
The beneficial properties of glucose are to provide the energy the body needs. This benefit is also seen in fats and glucose as carbohydrates. The component is found in the following groups of useful foods:
- bread products;
- fruit;
- vegetables;
- milk products.
The benefits of sugar are obvious. The harm is noted when an excess amount of a substance enters the body.
The benefits of glucose for the body
The substance is essential for basic metabolic processes in the body. The brain needs sugar. With its lack, a feeling of hunger arises, which is a kind of signal.
Half of all energy a person receives through the beneficial processes of converting sugar. It initially undergoes hydrolysis. In this phenomenon, 2 molecules of the so-called pyruvic acid are formed from 1 glucose molecule.
The beneficial properties of sugar are distinguished:
- energy source;
- an element of blood substitutes, anti-shock medications;
- eliminates stress;
- component of metabolic processes;
- contributes to the adequate functioning of the heart;
- improves overall well-being.
What foods contain glucose
Dextrose can be found in many beneficial foods. Glucose is part of the blood.Eaten foods are broken down into the following components:
- proteins;
- fats;
- carbohydrates.
It is known that carbohydrates are broken down into fructose and glucose. A significant amount of the substance is contained in the following products:
- candy;
- honey;
- berries and fruits;
- beans, lentils, beans;
- cereals;
- sugar;
- White bread;
- cabbage;
- carrot;
- pumpkin.
Sugar in the form of starch can be found in boiled potatoes and corn. Honey includes not only glucose, but also beneficial fructose.
Daily intake
Significant amounts of dextrose are harmful. The daily intake, which is beneficial, is 30-50 g. Experts recommend consuming less sugar. This is necessary in order to stimulate the production of monosaccharides by the body from various foods.
Normal blood glucose
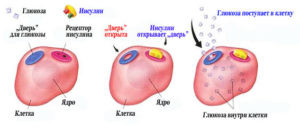
The human body processes dextrose daily. This process is observed during food intake due to the functioning of the pancreas, which produces hormones. Insulin as well as the liver controls blood sugar levels.
In diabetes mellitus, the required insulin is not produced. Insulin injections help control blood sugar levels.
Most people test using a home sugar system.
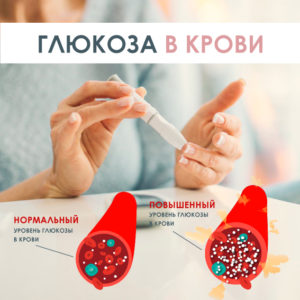
The body's performance largely depends on the concentration of sugar in the blood. Pre-meal glucose levels range from 90 to 130 mg / dL. After 1-2 hours, the concentration of the substance should be no more than 10 mg / dl.
The norm of blood glucose in children (up to 14 years old) ranges from 3.3 to 5.5 mmol / l. in adults (14-60 years old) this indicator increases. The glucose norm in men is from 3.3 to 5.5 mmol / l. Age, not gender, is the determining factor. The glucose rate in women is the same as in men.
The table includes information that reflects the rate of blood glucose.

Symptoms of a lack of glucose in the body
Hypoglycemia can cause serious health damage. This pathological condition is manifested by signs associated with the properties of dextrose:
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- headaches;
- pallor of the skin;
- rapid pulse.
Hypoglycemia can act as a consequence of diabetes and an independent symptom. Indicators fall to 2.5 (men) and 1.9 (women) mmol / l. When dizziness, clouding of consciousness appears, you need to take food, for example, a bun. This will allow the sugar level to rise to the desired level and eliminate the corresponding symptoms.
Why high blood glucose is dangerous
The following factors are distinguished that lead to an increased level of glucose in the blood:
- heavy food;
- stressful condition;
- somatic pathologies;
- lack of physical activity;
- a pass in taking medications for diabetes mellitus.

An increase in the permissible level of a substance can lead to weight gain, the development of diabetes mellitus and other diseases. In such cases, a diet is required to lower the glucose concentration, which can be harmful.
Nutrition for hyperglycemia
Against the background of hyperglycemia, an increase in the permissible blood sugar level is observed. The harm is caused by the occurrence of dangerous complications. Endocrinologists call the following useful products to reduce the concentration of glucose in the blood:
- seafood: crabs, lobsters, lobsters;
- soy cheese;
- walnuts and other nuts: cashews, almonds, peanuts;
- spinach;
- tomatoes, turnips, olives, ginger (root), cucumbers, olives, Jerusalem artichoke;
- black currant;
- lettuce, cabbage, zucchini, pumpkin;
- oatmeal;
- grapefruit, lemon;
- cinnamon;
- flax oil and seeds;
- legumes;
- blueberries, watermelon, cherries, avocado;
- potato juice (young) and sauerkraut;
- green tea;
- dairy products (cheese, butter);
- onions (baked) and garlic, mushrooms;
- meat (chicken), fish;
- tea with the addition of rose hips, black currants, hawthorn.
Instructions for the use of glucose tablets
In medical practice, tablets are prescribed in the following cases:
- insufficient intake of carbohydrates with food;
- hypoglycemia;
- dehydration with diarrhea and vomiting;
- poisoning.
The benefits of glucose syrup are achieved when using isotonic and hypertonic solutions. This form can also be used as a diluent for certain medicines.
With diabetes mellitus
Glucose tablets can be both beneficial and harmful. Medication is usually not prescribed for diabetes. The exceptions are cases when it is necessary to urgently increase the concentration of a substance. Hypoglycemia develops with an overdose of insulin.
Experts pay attention that the tablet form is considered optimal for diabetes. The main positive properties of drugs in tablets are called:
- high speed of impact;
- predictability of the result.
A glucose solution is recommended for severe hypoglycemia.
Athletes
The use of the substance in the form of tablets is useful for intense physical exertion. Muscles need dextrose in order to quickly replenish the expended energy. Benefits can be expected if the drugs are taken 1-2 hours before the start of training. This usage pattern is related to the properties of sugar.
There is a special scheme for taking a useful substance. 7 tablets (1 g each) are dissolved in a liter of water. It is necessary to drink 3-4 glasses of the resulting solution with an interval of 1 minute.
In case of poisoning
In order to eliminate the consequences of poisoning, dextrose is used in the form of tablets. The benefits of glucose are achieved when the drug is administered intravenously.
Glucose is indicated for poisoning with poisons (hepatotropic) of moderate or moderate severity:
- carbon tetrachloride;
- aniline;
- paracetamol.
Side effects
The benefits and harms of glucose for the human body is the risk of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. Excessive consumption of confectionery can lead to obesity and other serious consequences that are associated with the properties of sugar. However, hypoglycemia is also not a beneficial condition. Pathology causes a deterioration in well-being, decreased performance, and light-headedness.
After using dextrose, harm may occur in the form of an increase in cholesterol concentration. This property is dangerous by the formation of blood clots and the development of thrombophlebitis.

Against the background of the use of sugar in various dosage forms, the following undesirable reactions may occur, which are harmful to health:
- decreased appetite;
- left ventricular failure;
- hypervolemia;
- dyspepsia;
- feeling of thirst;
- nausea;
- flatulence.
Contraindications to the use of glucose
The use of drugs can be harmful in the following cases:
- allergy to the components of the medication;
- hyperglycemia;
- hyperlactacidemia;
- a circulatory disorder that can lead to pulmonary or cerebral edema;
- edema of the brain, lungs;
- postoperative disorders manifested by glucose utilization disorder;
- acute form of left ventricular failure.

Medicines can be prescribed with caution against the background of pathologies:
- chronic decompensated heart failure;
- chronic renal failure;
- hyponatremia (decrease in the permissible sodium concentration).
Conclusion
The benefits and harms of glucose allow it to be used for prophylactic and therapeutic purposes. Useful properties determine the use of the component as a detoxifying agent.

