Content
The effect of the preservative nisin on the body is not felt if its consumption does not exceed the maximum permissible daily intake. Immediately after the discovery of the substance in 1944, it was used as an antibiotic in the treatment of gastrointestinal problems. But with the advent of more effective drugs, nisin firmly moved into the category of food additives and received the number E234.
Lowland composition
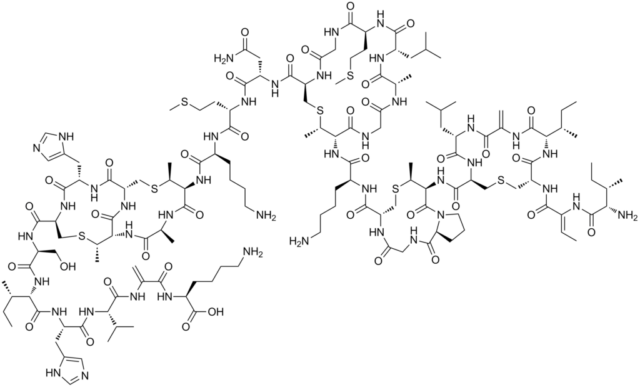
The E234 preservative contains only one active ingredient: the antibiotic nisin. He has a complex formula. The polymer molecule consists of 29 amino acids. Not all of them are found in proteins. Chemical formula E234: C₁₄₃H₂₃₀N₄₂O₃₇S₇. In fact, it is a product of the vital activity of bacteria Streptococcus lactis, more precisely one of the species: lactococcus lactis (Lactococcus lactis). The rest of the substances present in the package with the food additive play the role of a filler and do not matter.
Production technology
Nisin is one of the natural antibiotics that arose during the interspecies struggle between lactobacilli. In an effort to provide itself with living space, lactococcus lactis "learned" to produce substances that inhibit the growth and reproduction of other representatives of lactic acid bacteria. Man only put this ability at his service.
Bacteria are also grown on natural substrates: dextrose or milk. The only difference from the natural process is the gene modification of this type of microorganism. Today, there are already several artificially derived strains of lactococcus.
It was approved as a safe food preservative in 1969.
The health benefits of lowland
There is no benefit to the body from the use of nisin in food. In addition to the preserved nervous system. Because there is no need to throw away the products that are spoiled after two days and spend money on new ones. There is a maximum allowable daily intake of this antibiotic, at which it is not harmful. But it is very difficult to calculate the amount of E234 supplement eaten, since it is added to many different products.
The harm of the preservative nisin
Nisin, like any other antibiotic, "does not know how" to divide bacteria into useful and harmful. It inhibits the development of all microorganisms. Because of this effect, the maximum concentration of the preservative in food has been established. There is also a maximum daily dose of E234 for humans. But due to the widespread use of the food additive in a wide variety of foods, this dose is very difficult to control.

Application area
The preservative has long "left" the category of medicines and has firmly taken its place in the food industry. It allows the manufacturer to extend the shelf life of their products. E234 additive has penetrated almost all areas of food production. It is most popular at bakeries. But, if you carefully read the fine print on the label, sometimes it can even be found in wine.
Application in the food industry
Due to the ability of E234 to withstand high temperatures without compromising effectiveness, the preservative is used in almost all processed products, from bakery products to alcoholic ones. The preservative retains its properties in an acidic environment. Contains lowlands:
- milk products;
- bakery and confectionery products;
- fish semi-finished products and ready meals;
- sausages, pates;
- beer;
- wine.
None of the packages indicate the amount of nisin in percent or grams.
Terms and conditions of storage
The preservative can be packaged in packages of different sizes. It depends on the needs of the enterprise. For example, bakery products are produced in small private bakeries and in large factories that supply the entire city with products. But the storage conditions are the same in all cases: in a dry, dark place. The air temperature should be 4-25 ° С.
To surely protect the lowlands from direct sunlight, the bag with the preservative is additionally wrapped in thick paper. On the top layer of the packaging, information about the manufacturer, date of manufacture and batch number are indicated.
Conclusion
The influence of the preservative nisin on the body is today recognized as negligible. However, the maximum daily dose has been established. If it is possible to eat foods without the food additive E234, it is better to do without it. Although this weak antibiotic is not capable of causing serious harm to health.

