Content
- 1 Compatibility of vitamins B12 and folic acid
- 2 Deficiency of vitamins B12 and folic acid
- 3 Foods containing vitamin B12 and folic acid
- 4 Preparations with folic acid and vitamins B12
- 5 Indications and contraindications for drugs with folic acid and vitamins B12
- 6 Rules for the use of vitamins with folic acid and B12
- 7 Conclusion
- 8 Reviews of folic acid with vitamins B12
In medical practice, the combined intake of folic acid and vitamin B12 is often used. This is due to the mechanism of their synthesis, the ability to enhance the action of each other. Reviews of folic acid with vitamins B12 indicate the effectiveness of the parallel use of nutrients.
Compatibility of vitamins B12 and folic acid
Minerals and vitamins ensure adequate functioning of the body. One of the important elements experts call folic acid or vitamin B9. It is also considered a female component due to its effect on reproductive function.
Folic acid is a water-soluble element that is involved in hematopoiesis and DNA production of cells. The component comes with food. The intestinal microflora synthesizes folic acid.
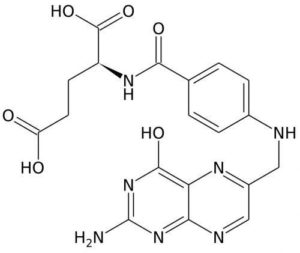
Folic acid is essential for increased division of cellular DNA elements during pregnancy and lactation. Sufficient intake of the component is considered to prevent the development of intrauterine pathologies of the embryo and fetus. During pregnancy, the intake of vitamin B9 is 0.6 mg (per day).
Adequate assimilation of nutrients by the body ensures their correct combination. For example, folic acid is compatible with vitamin B12. These components are involved in the production of amino acids.

Deficiency of vitamins B12 and folic acid
Vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) deficiency is called B12-deficiency anemia. However, B12 folate deficiency anemia also exists.
Megaloblastic anemia leads to a breakdown in the production of DNA, which are responsible for the proliferation of cellular elements. In pathology, violations are noted on the part of the hematopoietic cells of the skin, mucous membranes of the digestive tract, and the brain. Anemia is characterized not only by a decrease in the level of hemoglobin and erythrocytes, but also by monocytes, neutrophils, reticulocytes and platelets.
These disorders are interrelated, since vitamin B12 is required for the formation of active folic acid. For the production of thymidine, which is considered a constituent of DNA, folic acid is needed. With a deficiency of vitamin B12, synthesis stops, and defective DNA is formed. Thus, the defective DNA is destroyed rather quickly, which causes the death of cellular tissue elements.
The reasons for the deficiency of important components include:
- unbalanced nutrition, in which a sufficient amount of vitamins does not enter the body (a diet with a predominance of plant foods);
- chronic alcoholism, often accompanied by cirrhosis and hepatitis;
- complete removal of the stomach;
- Crohn's disease, bowel cancer, celiac disease;
- the presence of parasites;
- malfunctions of the pancreas;
- Imerslund-Gresbeck syndrome;
- advanced age;
- pregnancy;
- skin pathologies;
- taking anticonvulsants.
Symptoms of a deficiency include:
- deterioration in performance and increased fatigue;
- fainting against the background of intense physical activity;
- hypotension;
- dizziness and headaches;
- increased heart rate and pain;
- yellowish skin tone;
- glossitis or inflammation of the tongue;
- enlargement of the liver, spleen;
- swelling of the legs;
- stool disorders;
- distortion of taste;
- the appearance of mouth ulcers;
- loss of appetite and weight loss;
- exacerbation of gastritis;
- depression;
- weakening of muscles.
Foods containing vitamin B12 and folic acid
Water-soluble substances produced in the intestine are absorbed through food or drugs. Foods rich in vitamin B12 and folate are readily available. However, one should take into account their insignificant resistance during heat treatment.
The participation of useful components in the following processes is noted:
- carbohydrate and fat metabolism;
- the functioning of the nervous system and liver function;
- the formation of a neural tube in the fetus (during pregnancy);
- effect on blood clotting;
- lowering cholesterol concentration;
- increased appetite;
- improving memory;
- prevention and treatment of anemia;
- normalization of pressure;
- antiallergic effect.
Vitamin B12 includes animal products. Fruits and vegetables do not contain cyanocobolin, but contribute to its production.
The maximum content of vitamin B12 is noted in the following products:
- liver (chicken, pork, beef);
- chicken;
- cheese;
- eggs;
- herring;
- kefir;
- sardine.
Folic acid contains products of animal and plant origin:
- spinach;
- corn;
- beet;
- potatoes;
- avocado;
- asparagus;
- buckwheat;
- beans;
- kiwi;
- sesame;
- Walnut;
- peanut;
- liver (pork, cod);
- cow's milk;
- butter and cream;
- curdled milk;
- chicken egg.
Preparations with folic acid and vitamins B12
Components Benefit:
- the immune system;
- reproductive organs;
- Central nervous system;
- the brain;
- skin.
Preparations with folic acid and vitamin B12 are highly effective. This is due to the complementary combination of components. Medicines are used both for therapy and for the prevention of vitamin deficiency. To eliminate the deficiency of elements, you can use mono-remedies and complex preparations.
Folic acid is available in the following forms:
- drops;
- capsules;
- tablets.
Doctors prescribe the following drugs that combine folic acid and vitamin B12:
- Now Foods (250 tablets). The complex supports the metabolism of homocysteine. This dietary supplement is a kosher product that is also suitable for vegans and vegetarians. According to the instructions for use, dietary supplements are taken daily, 1 tablet.

- Bluebonnet nutrition (59 ml). The drug is in liquid form. This vegan product is gluten free. The food supplement is taken 1 ml per day.

- Superior source (60 tablets). The dietary supplement does not contain GMOs. To fill the lack of nutrients per day, it is necessary to dissolve 1 tablet.

- Thompson (30 tablets). The tool is taken 1 tablet once a day.

Most drugs include a combination of vitamins B6, B9 and B12:
- Mason natural (with calcium);

- KAL;

- Superior source (with stevia).

Popular B-complexes include:
- Nature's Bounty;

- California Gold Nutrition;

Indications and contraindications for drugs with folic acid and vitamins B12
Folic acid intake is indicated in the following cases:
- treating anemia;
- replenishment of the lack of a substance (for example, with an unbalanced diet);
- prevention of the development of fetal anomalies.
Possible side reactions include:
- nausea;
- allergic reactions;
- bloating;
- bitterness in the mouth.
With the simultaneous reception of the components, the following effects are achieved:
- increased production of choline;
- amino acid production;
- synthesis of nucleic acids.
There are the following indications for the appointment of vitamin B12 as a means of monotherapy:
- depressive conditions;
- stabilization of the functioning of the nervous system;
- acceleration of regeneration;
- improving memory.
The simultaneous intake of folic acid and vitamin B12 supports the nervous system, prevents depression, and strengthens the immune system. The vitamin complex is prescribed as part of complex therapy for hypotension, bronchial asthma and sclerosis.
Rules for the use of vitamins with folic acid and B12
It is advisable to start using the funds after the identified avitaminosis of folic acid and cyanocobalamin, which is associated with their action. With monotherapy, vitamin B12 deficiency is initially replenished. Usually anemia is an indication for intravenous drug administration. In case of iron deficiency, appropriate medications are also prescribed.
Conclusion
Reviews of folic acid with vitamins B12 testify in favor of the effectiveness of their complex use. The components perform important functions in the body, supporting the adequate functioning of organs and systems.
Reviews of folic acid with vitamins B12
Reviews contain the necessary information about the indications for the appointment of vitamins B9 and B12, their effectiveness.

